By: Warren Gray
Copyright © 2023
“It does everything. It goes everywhere. It’s as faithful as a dog,
as strong as a mule, and as agile as a goat. It constantly carries
twice what it was designed for, and still keeps on going.”
— Ernie Pyle, Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist
“Jeep is a synonym for adventure. These vehicles help
you to go beyond the limits, and test the impossible.”
— Jeep advertisement
“Don’t follow me. You won’t make it where I’m going.”
— Bumper sticker on Jeep
The famous, combat-proven Jeep was designed in 1941 by Willys-Overland as the world’s first mass-produced, light, four-wheel-drive motor vehicle, which became the primary, multi-role vehicle of the United States military and its allies in World War Two. U.S. Army Chief of Staff General George C. Marshall called the Jeep, “America’s greatest contribution to modern warfare.” From 1942 to 1945, a total of 647,925 were produced, including 359,489 Willys MB Jeeps and 277,896 Ford GPW (General Purpose, Willys-license) Jeeps. Joe Frazer, the president of Willys-Overland at that time, claimed to have coined the word “Jeep” by slurring the initials “G.P.”
Initially, it was powered by a 2.2-liter, four-cylinder, inline, Willys L134 “Go-Devil” engine, producing 60 horsepower, with a three-speed, manual transmission, and a maximum speed of 65 miles per hour. It weighed in at a modest 2,453 pounds fully fueled, and was only 62 inches wide, quite narrow by today’s standards, but able to fit into tight spaces between fallen debris in battle. Its distinctive seven-slotted front grille was actually designed by Ford engineers (originally with nine slots) under a Willys production license and was later trademarked by Willys for all subsequent Jeep products.
Perhaps the most glamorous and well-known use of the Willys MB Jeep was as a fast-attack vehicle, initially in North Africa in 1942, with British Special Air Service (SAS) commandos on long-range reconnaissance raids in the desert. They traveled in groups as small as two vehicles, or often as large as 50 to 60 Jeeps, armed with a variety of .303-caliber Vickers-K machine guns and/or Browning M2 heavy machine guns, mounted upon an M31 tubular pedestal in the back. A total of 31,653 M31-equipped Jeeps were manufactured, but even without this rear mount, many Jeeps were converted to carry machine guns in the front and rear.
From 1964 to 1968, the American TV series, “The Rat Patrol,” starring Christopher George, featured the daring exploits of three U.S. soldiers and one British sergeant, whose mission was “to attack, harass, and wreak havoc on Field Marshal Rommel’s vaunted Afrika Korps.” The show was not historically accurate, since virtually all such actual missions during World War Two were entirely British, but “despite its many historical inconsistencies, the show achieved successful ratings at a time when military shows were in decline because of public disaffection with the Vietnam War,” according to Wikipedia. It was certainly a dramatic and exciting program, featuring a pair of high-speed, heavily-armed Willys MB Jeeps in the desert.
Later, during the Korean War, Willys Motors introduced the redesigned Willys MD (M38A1) Jeep in 1952, with more-rounded corners, which also formed the basis for the civilian and commercial Jeep CJ-5 series (built from 1954 to 1983), the world’s first mass-produced, four-wheel-drive civilian cars. The Willys MD was powered by a 2.2-liter, four-cylinder, inline, Willys F134 “Hurricane” engine (75 horsepower), with a three-speed, manual transmission. Overall weight increased to 2,660 pounds, but the width narrowed to just 60.8 inches.
It was produced from 1952 to 1971, and served with the U.S. Army until 1960, but it was also exported to at least 29 countries (including Canada, Egypt, Israel, Iran, Jordan, Lebanon, the Netherlands, Pakistan, South Korea, Switzerland, Taiwan, and Turkey), and served in numerous wars up through 1991. A total of 101,488 MD models were produced, but there were also 155,494 very similar Jeep CJ-3B models produced.
A competing design from the Ford Motor Company in 1951 was the M151A1 utility truck, looking almost exactly like a Willys Jeep, except for a horizontally slotted grille, versus the original vertical slots. It was, however, a completely new design, with many structural differences, including fully independent suspension with coil springs, but with similar performance. It featured a 71-horsepower engine with four-speed transmission, weighed 2,400 pounds, and was three inches wider, at 64.3 inches. But, because of the independent, rear suspension, it had an unfortunate tendency to roll over during hard turns, and this was corrected with the M151A2 model, introduced in 1968, with semi-trailing arm rear suspension.
The M151 Jeep entered U.S. Army service in 1960, and was used in active service well through the 1980s, until it was replaced by the AMC Hum-vee, and the last Army M151A2 was retired in 1999. It was exported to at least 100 countries worldwide, including 15 NATO nations, with over 100,000 produced. At least three different Fast-Attack Vehicle (FAV) configurations were produced, seeing action in numerous wars between 1960 and 1999.
The vaunted combat-veteran Jeep, however, has never been fully retired, and it is still produced, from 1990 to this very day, as an off-road, military vehicle in Upper Nazareth, Israel, as the AIL (Automotive Industries, Limited) Storm (Sufa, in Hebrew). These are military derivatives of the Jeep Wrangler model, with the M-240 Storm I made from 1991 to 1996, featuring an AMC four-liter, six-cylinder engine producing 180 horsepower.
In 2006, the M-242 Storm II (or “Storm Commander”) was introduced, with a four-door body and six-speed, manual transmission, or optional, automatic transmission. Finally, from 2008 to the present day, the Storm III was produced, with a 2.8-liter, VM Motori (Italian) four-cylinder, turbodiesel engine, with 158 horsepower, based upon the Jeep Wrangler JK design. The Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) have acquired at least 100 Storm II models and 600 Storm III (since 2011) models, which have proven especially useful in patrolling the tight confines of ancient, walled villages in the Middle East.
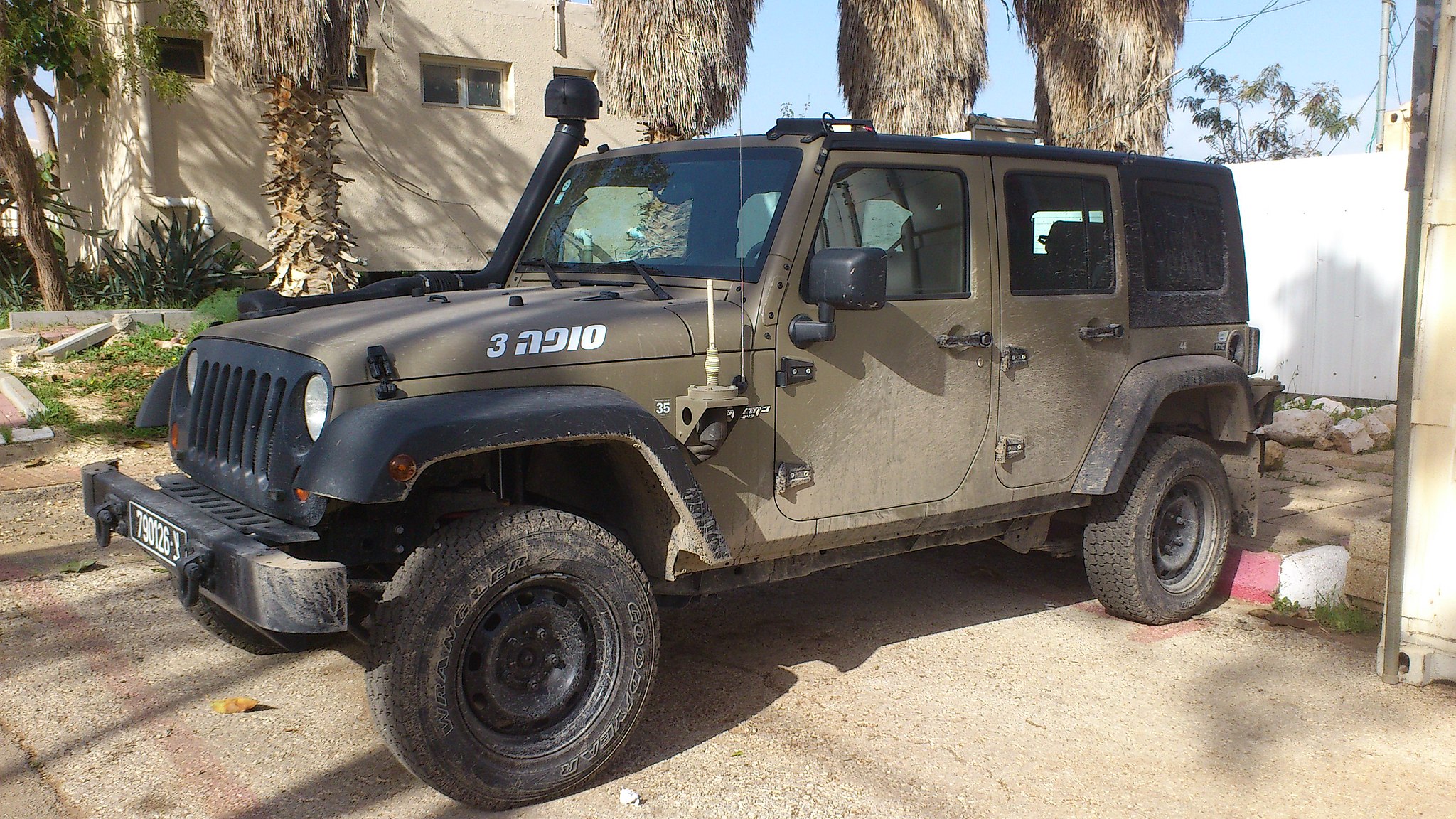

קרלוס הגדול, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The very latest incarnation of the time-honored, military Jeep is the new, J8 model, also based upon the Wrangler JK and JL platforms, introduced in 2007, and assembled in Gibraltar by Africa Automotive Distribution Services Limited (AADS), and in Israel by AIL of Nazareth, under license from Chrysler. It’s essentially a Storm III with several more options available, and it’s already been exported to Belize, the Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Ghana, Guatemala (1,020), Mongolia, Panama, Peru, Taiwan (3,598), and Tajikistan.
A VM Motori engine boasting 197 horsepower is standard, with a five-speed, automatic transmission, but a 260-horsepower, V6 engine is available, with an eight-speed, automatic transmission. A pair of production J8s was tested by Israeli web magazine Jeepolog.com journalists in April 2009, and they proclaimed the new J8 to be “probably best Jeep ever.”

Jeep J8 Wrangler Command Vehicle. Photo credit: AADS

Jeep J8 fast-attack vehicle (FAV) configuration. Photo credit: Military-Today.com
So, while the world-famous military Jeep has been retired from U.S. Army service for nearly the past quarter-century, it bravely soldiers on in Israel, Egypt, Guatemala, Taiwan, and many other countries around the world, as rugged and durable as ever, still serving in a multitude of utilitarian roles, from transport, to ambulance, to fast-attack vehicle. In fact, the Jeep J8 was recently submitted as a proposed replacement for the AMC Hum-vee for the U.S. Special Forces. Even on today’s remote battlefields, there’s still nothing quite like a Jeep!
* * *
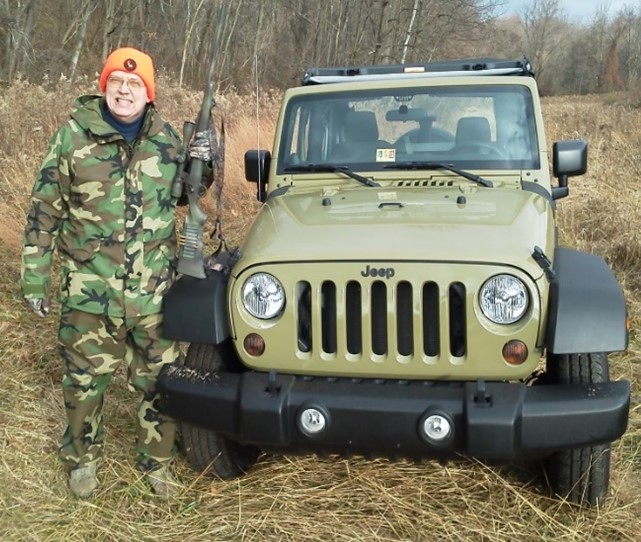

Author hunting with Remington 700 ADL rifle and 2012 Jeep Wrangler, November 24, 2012.
Warren Gray is a retired, U.S. Air Force intelligence officer with experience in joint special operations and counterterrorism. He served in Europe and the Middle East, earned Air Force and Navy parachutist wings, four college degrees, and was a distinguished graduate of the Air Force Intelligence Operations Specialist Course, and the USAF Combat Targeting School. He is currently a published author, historian, and hunter. You may visit his website at: warrengray54.vistaprintdigital.com